ONE-STOP ELECTRONIC COMPONENT DISTRIBUTOR for Active Component and Passive Component
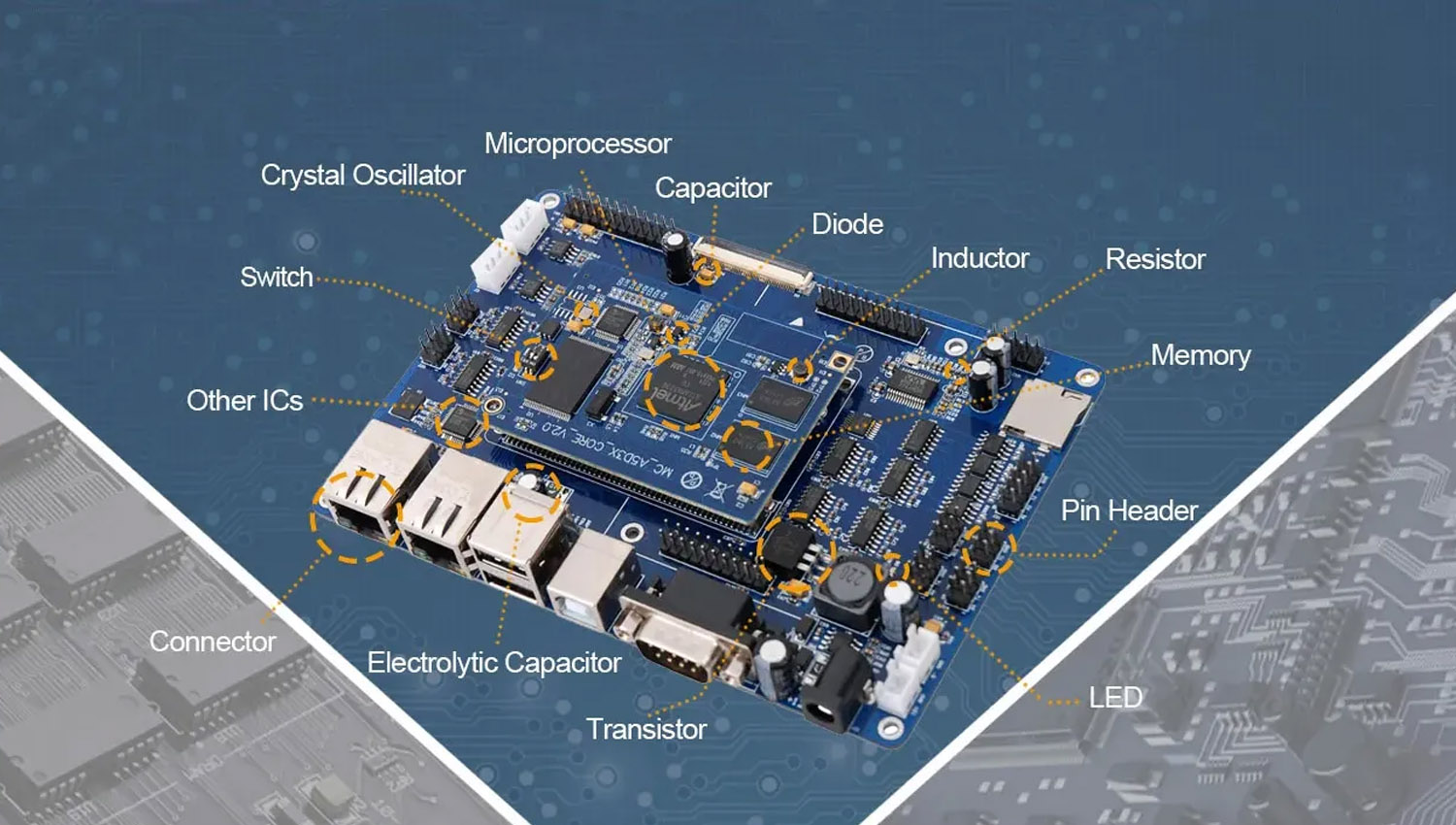
our company distributes a comprehensive set of passive electronic components to manufacturers across sectors and applications. We have the resources and tie-ups to source high quality, reliable, robust and high-performance electronic components like Chip Resistors, Chip capacitors (MLCC), Electrolytic Capacitors, Inductors and Crystals, from global OEMs.
also we have provide active components like Microcontrollers, Amplifiers, ADC and DAC converters, Clock & Timing devices, Data devices, Diodes, Embedded Devices, Interface, Logic IC’s, Memory devices, Multiplexers, Power management devices, Temperature sensors, Transistors and Voltage regulators.
we promises that all products originate from the original distribution channel.
We provide original electronics parts with one-stop BOM service.
Main supply products include:#Integrated Circuit, #Transistor, #Resistor, #Capacitor, #Inductor, #Diode, #Crystal Oscillator,#Potentiometer
Our strong brand: #Infineon, #NXP , #TexasInstruments , #STMicroelectronics, #XILINX , #INTEL , #MICROCHIP, #onsemi, #TE ,#UTC ,etc.
HongKong NiuYi Co.,Limited (ZRH Electronics)
China Headquarter: Room 14B,14 Floor,Block A,Xiandai Window Building,Huaqiang North Road,Futian District,Shenzhen City,Guangdong Province,China
tel:(86) 755-83253306
Korea Division:Rm.1009, 10, Gyeongin-ro 53ga-Gil, Guro-Gu, Seoul, (Guro-dong, DaeMyung Valeon), 08214, Korea
tel:(0082) 010-6318-1889